IPC-200 - Industrial process control
The modular and flexible training equipment to be skilled in the field of Industrial Process Control.
The modular and flexible training equipment to be skilled in the field of Industrial Process Control.
IPC-200 emulates a liquid production and bottling plant and includes the technologies used in continuous process industry, such as pneumatics, electric motors, sensors, continuous processes, programmable controllers, industrial communications, etc. Fully modular and flexible equipment, comprised of three modules which can work individually or as a complete process line. Various configurations can be created to adapt the IPC-200 equipment to our users different requirements and budgets.
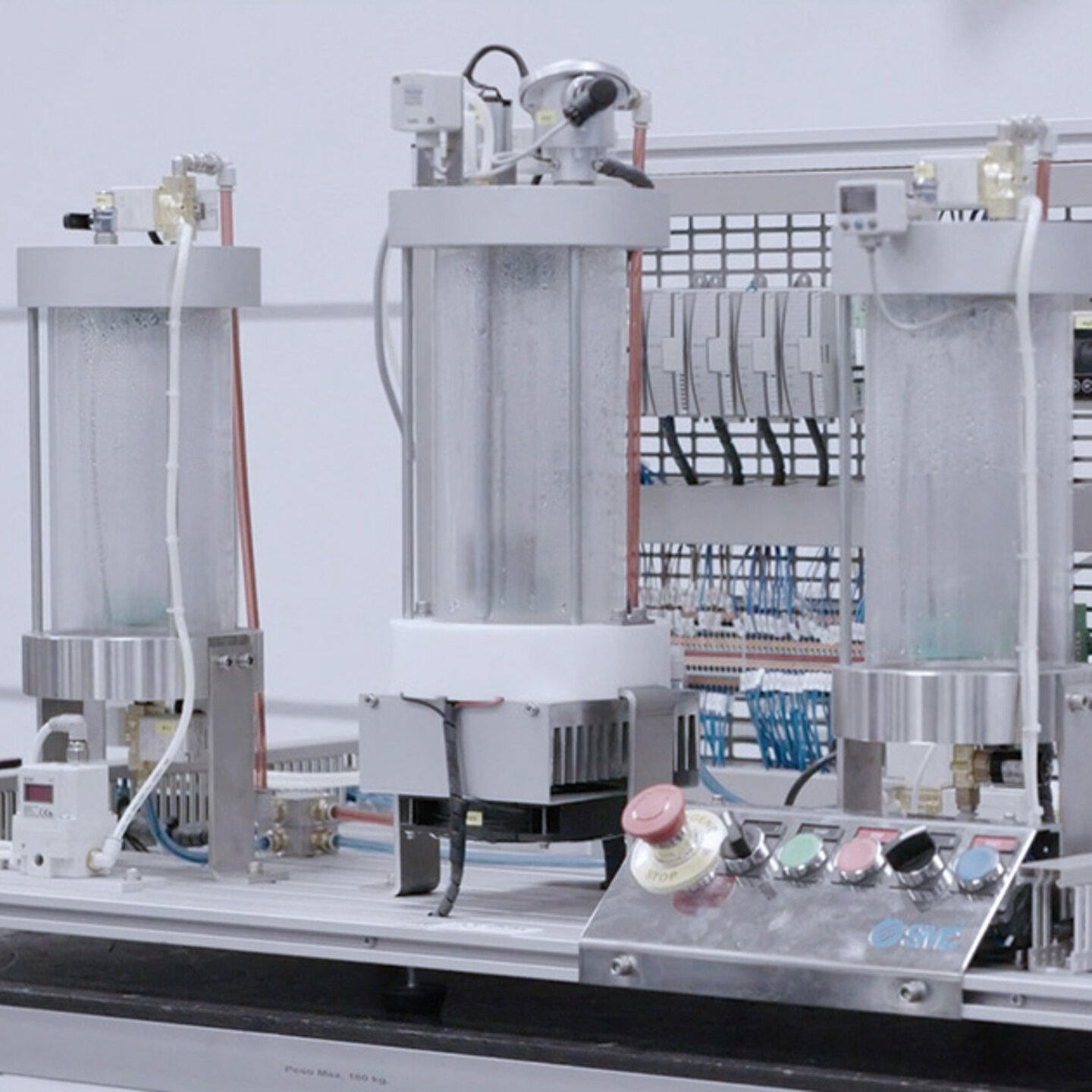
Image gallery

With this system you could...
