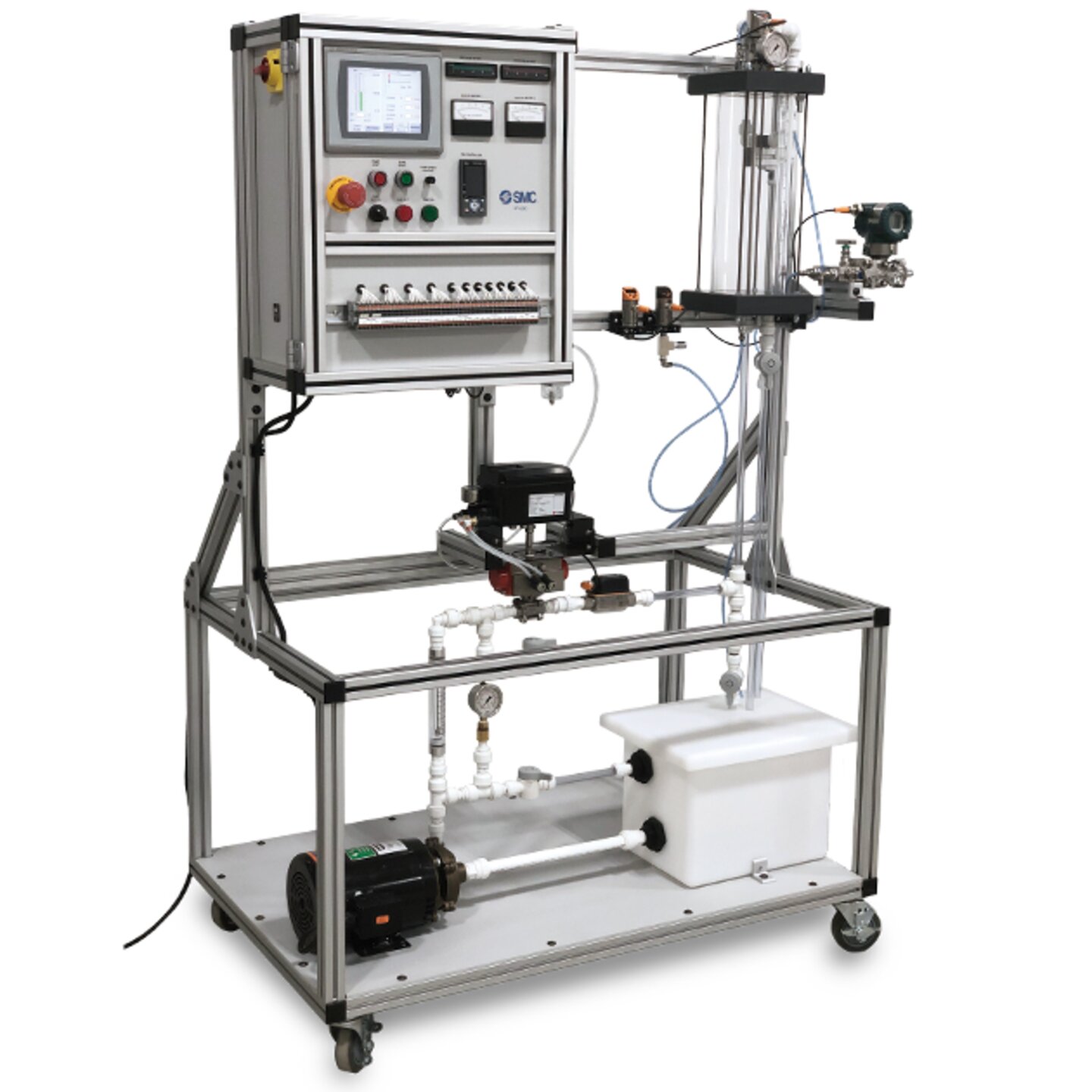
Why is process control technology important and beneficial to industry?
Some key features of this technology are:
- **Automation**: Process control systems can operate automatically, adjusting process variables without constant human intervention.
- **Accuracy and speed**: Process control technology can respond quickly to changes in the process and adjust conditions to keep variables within desired limits with high accuracy.
- **Security**: Helps ensure the safe operation of industrial processes by preventing hazardous or unsafe conditions.
- **Efficiency**: By keeping process variables within optimal ranges, greater operational efficiency is achieved, and costs are reduced.
- **Adaptability**: Process control systems can adapt to different situations and variations in process conditions.
Process control technology is applied in a wide range of industries, such as food, automotive, energy, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals and many others, where its use is crucial to maintain stable and safe operations and to achieve consistent, high-quality production.