RTS-200 - Robotics trainer
Discover the SMCs robotics training system that provides participants with a hardware platform for performing hands-on development for robotic operations.
Discover the SMCs robotics training system that provides participants with a hardware platform for performing hands-on development for robotic operations.
The RTS-200 training system provides participants with a hardware platform for performing hands-on development for robotic operations. The mobile platform includes various applications which can be quickly installed to provide advanced activities, expanding the learning objectives beyond simple pick and place functions. The design allows participants to advance from basic programming to integration of various technologies including electrical controls, pneumatics, controllers, artificial vision, sensors and more. It is a didactic trainer with a flexible design in which the user can develop skills in both, collaborative and non-collaborative, robotics technology. The system has different options that allow the user to configure the didactic equipment that best suits their needs. Within the robot integration options, it is possible to select the following parameters: It is possible to receive the didactic trainer with the robot fully integrated. For those users who already have a robot, there is also the possibility of integrating it themselves thanks to the instructions provided.
Elije la opción que mejor se adapte a tus necesidades y descubre cómo configurar tus referencias.
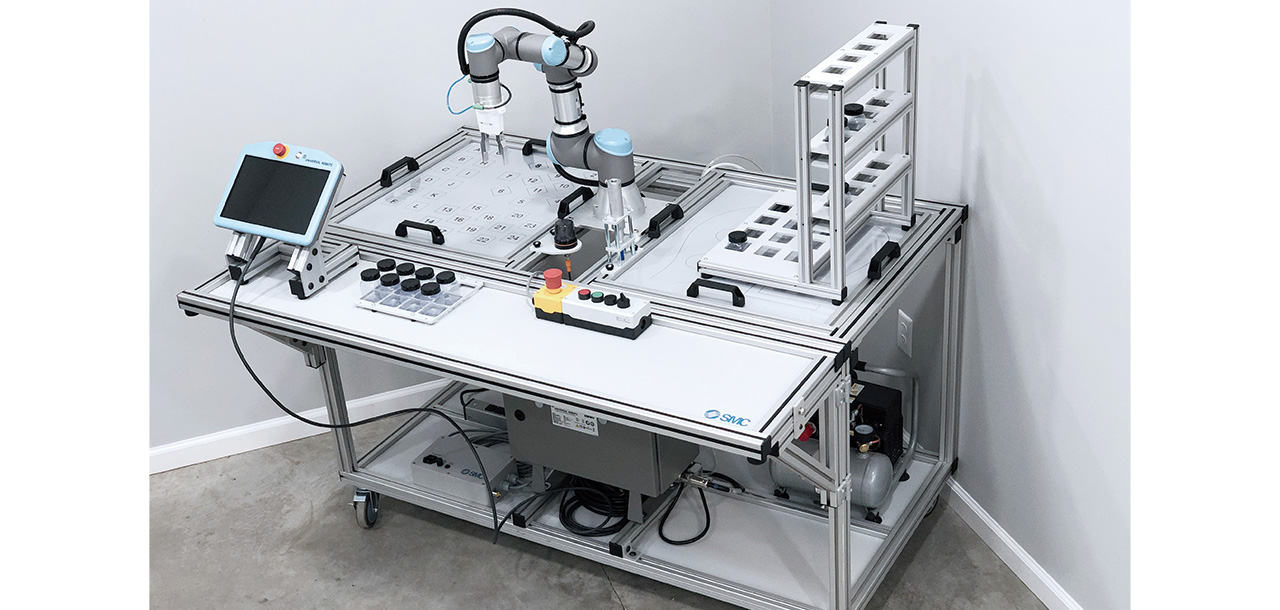
The RTS-200 robotics trainer has a series of applications through which the user can develop skills in relation to robotics technology. In addition to the basic installed applications, this didactic equipment also has a series of optional applications with advanced activities that extend the learning objectives: - Pneumatic Application and Part Transfer. - Integrated Sensors for part material, size, color and quality detection. - Production Application. - Variable Speed Conveyor with Sensors. - CNC Machine Tending (Simulated CNC). - Assembly Application. - Collaborative Assembly Application. All these applications are designed for quick and easy integration, to plug and play.
Image gallery
