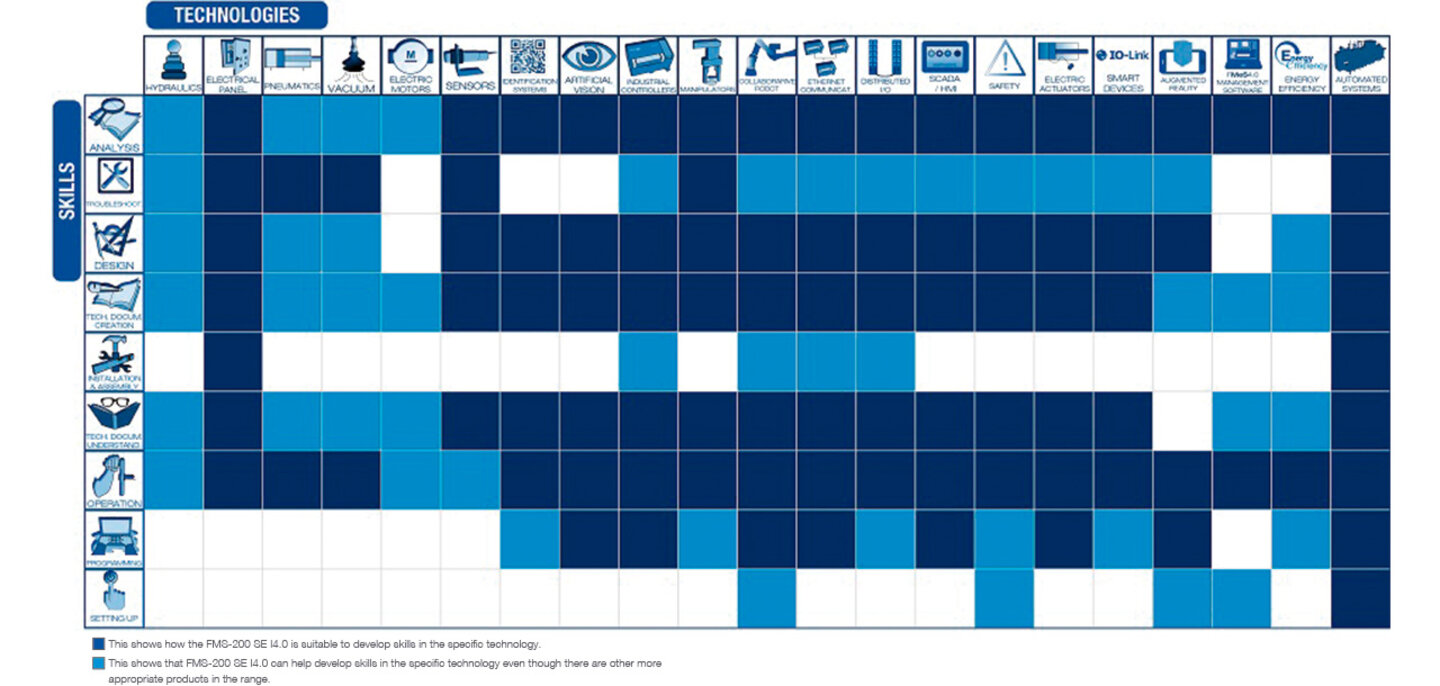
FMS-200 special edition with Industry 4.0 technologies
The training equipment, FMS-200 special edition - Industry 4.0, is the advanced mechatronics learning system for INDUSTRY 4.0.
The training equipment, FMS-200 special edition - Industry 4.0, is the advanced mechatronics learning system for INDUSTRY 4.0.
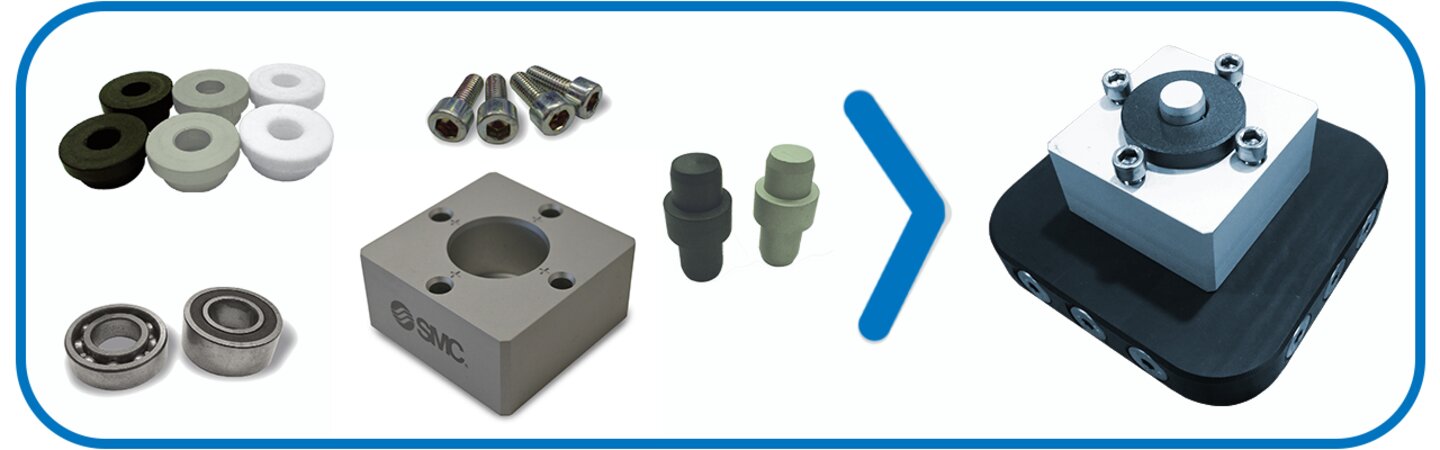
Advanced mechatronics training system in Industry 4.0. Increase your knowledge of industry 4.0 technologies and develop advanced skills in mechatronics utilizing a real industry-based platform. All the components in the FMS-200 Special Edition - Industry 4.0 are used in industry, so that the user works with real elements at all times making the learning process more meaningful.
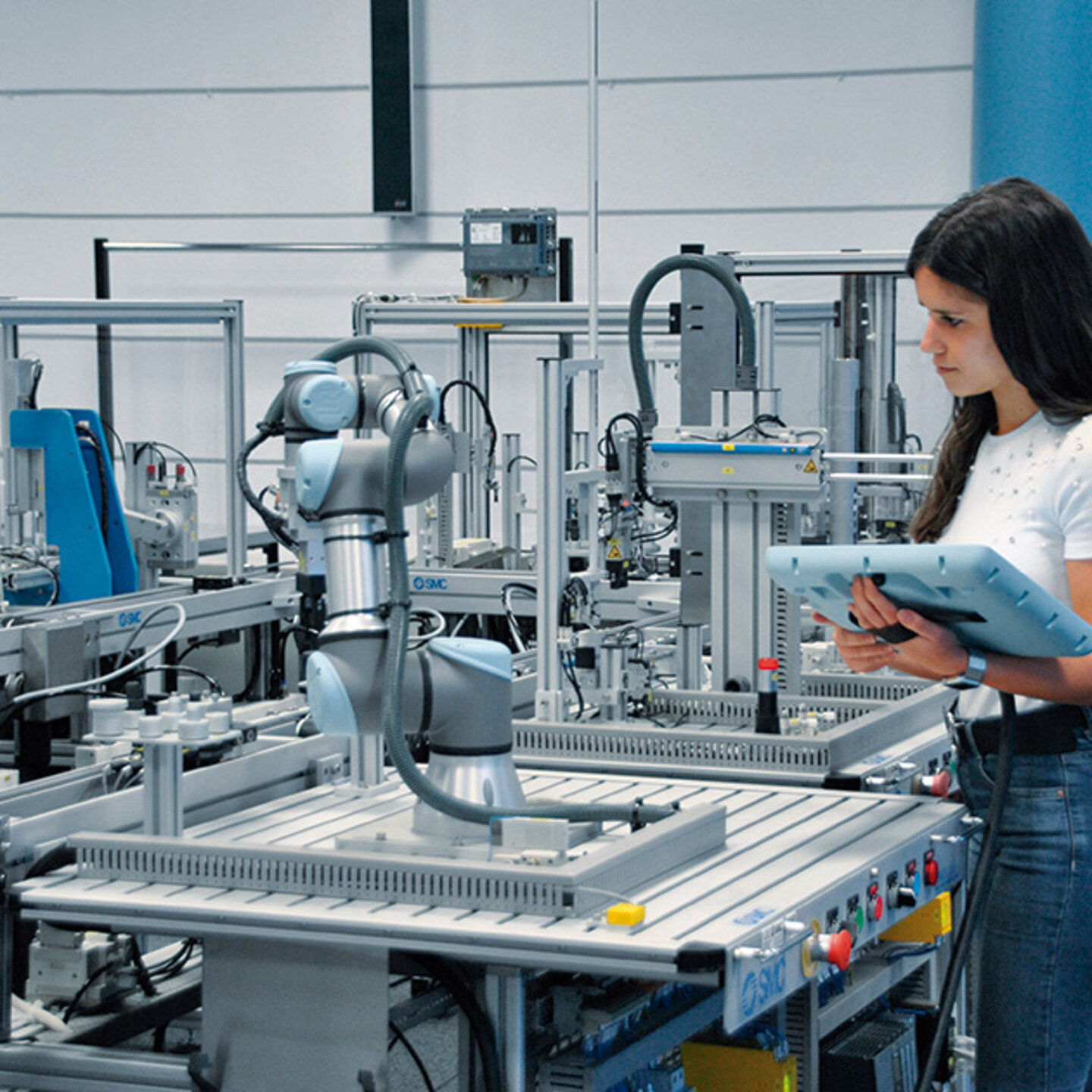

Image gallery



With this system you could...
Turning mechanism
